What is a VPN?
Types of Virtual Private Network (VPN)
Some of the standard types of VPNs are like:
1. Standalone VPNs:
It’s one of the most commonly seen VPN, which is widely popular among home users and small companies. It makes use of an application, which helps by creating an encrypted connection for the private company.
2. Extensions for Web Browsers:
Many VPN providers offer browser extensions or add-ons. Though, it comes with certain downsides like, it can provide online anonymity, only from a browser in which it has been installed. Moreover, many browser extensions are available these days. So, it’s best to check it and go with the one who offers other VPN services as well. Because, only VPN extension or a free VPN is quite likely to harvest user’s data, instead of its better to choose the reputed one and it’s also recommended to check the user reviews before getting it.
3. Corporate VPN:
Organizations who have employees working from remote locations, often make use of VPN which offers remote access. So, employees can work and access the company’s private intranet securely.
4. Router VPN:
It’s a different but quite popular VPN implementation method, which is used by companies who have a large number of devices to connect with router. The good part about having a VPN installed on a router is that it helps by saving you from installing a VPN on every device individually. Moreover, once its signed-in, router always stays connected to the VPN.
Likewise, connecting a router with a VPN is not as hard as it seems. You simply need to subscribe with the VPN plan of a provider who gives a VPN compatibility with a router and go through the VPN installation process offered by them.
Let’s understand How does VPN work:
How does VPN Works?
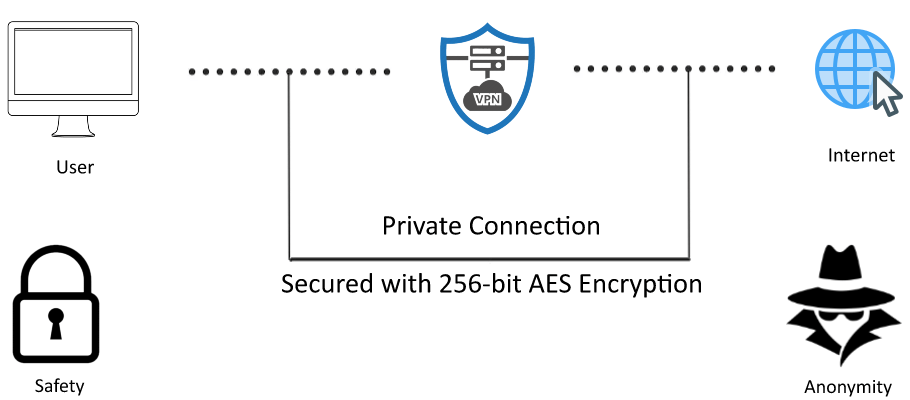
VPN creates an end-to-end connection between your device and the server. Once the connection is successful, all your data will be encapsulated into standard TCP/IP packets and then it will be transferred across the internet. As the data stays encrypted throughout the transaction, it stays completely hidden from cybercriminals, government and even your Internet Service Providers (ISP) and ultimately cannot gain any control nor can see the information.
In other words, VPN works as an inter-medium between public and the private network, where VPN works on behalf of the private network to provide anonymity and protection. So, whenever a local host sends data towards a host in a remote network, the data first pass through a private network via the protecting gateway device and then travel through the public network and finally pass through the gateway device which is protecting the destination host in the remote network. Moreover, VPN provides protection by encrypting it before it is sent through one private network to another, by encapsulating it into an IP packet which gets decrypted at the receiving end.
Let’s look at it with an example.
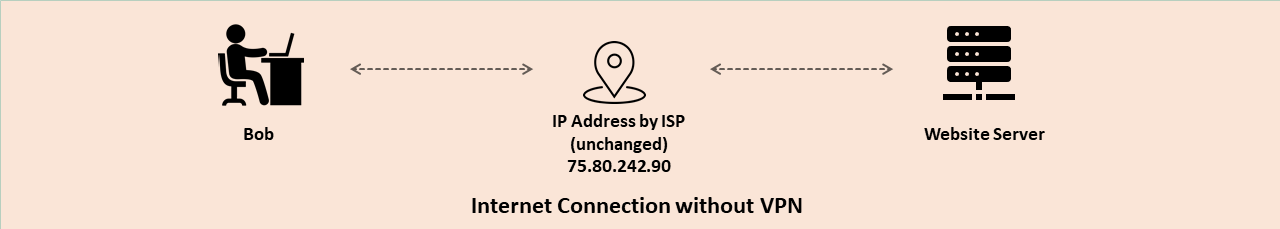
- Suppose Bob wants to access a website www.domain.com using VPN.
- First, he connects with a VPN application.
- When Bob is connecting with a VPN, he’s doing it with his original IP address.
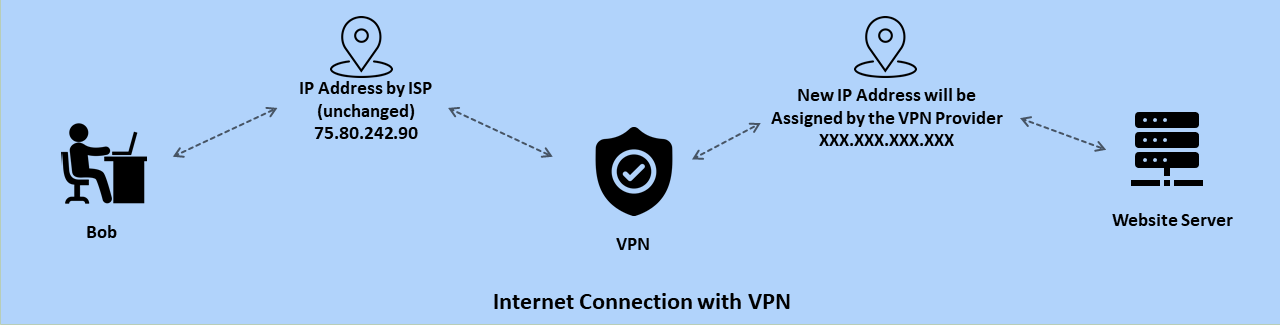
- Once the request of Bob is accepted by a VPN server, the VPN will try to access the website which Bob want to visit. But the twist is that it will do it with its VPN servers IP address and not of Bob. So, when the website sees the request, it will see it coming from the VPN server and not the Bob.
- As soon as, Website makes a successful connection with the VPN server, it will allow the access of website to a client and all the time connection between Bob and VPN & VPN and Website stay secured and encrypted.
- So, when Bob accesses a website www.domain.com using VPN. First, the request goes to VPN server with the users IP address and then VPN server sent it to the website using its own IP address and when any request is made by a website it is sent to a VPN server and VPN server send it back to the user.
Lastly, the VPN is not rocket science. It’s quite easy to use. Just go to your chosen VPN providers website and subscribe to a chosen plan. Once you’re subscribed you will have an option of
Application
Simply install your VPN providers application into your mobile phone and log-in. Select the server of a different country or state you want and connect with it. Once the connection is successful, simply browse the website you want, VPN will do its work in the background.
Web-Browser Extensions & Add-ons
Software
Is VPN Worth Having? What VPN Does for You?
Though, that’s not enough. As, malicious users, Internet Service Providers (ISP), or Government can still snoop into what activities users are doing. They can ultimately see all your activity, for example, which website user has visited. So, here good VPN services help you by providing anonymity. If you’re using a VPN, you can stay assured that your activity will also remain encrypted. It means no one will be able to know which website you’re visiting or what you’re doing, whether you’re using a public Wi-Fi or any ISP is trying to spy you.
Different VPN Protocols & Technologies
PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol):
Coined by Microsoft, PPTP is one of the oldest protocols which is used since the mid-1990s. It’s a networking standard, which is also used for connecting to virtual private networks (VPNs). However, PPTP itself is not responsible for providing encryption. Instead, it tunnels data packets, while encapsulating it using GRE protocol.
IPSec (Internet Protocol Security):
Comparatively, IPSec is a better option instead of PPTP. It’s a framework related to protocols which secure communications at the packet processing or network layer. In this packet, encapsulation and encryption are done with the ESP protocol and cipher algorithms like AES-GCM, HMAC-SHA1/SHA2, or 3DES-CBC.
L2TP (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol):
L2TP is an extension of the Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP), which is used by an ISP (Internet Service Provider) to enable the operations of a VPN over the Internet. Moreover, it’s used as an added security for tunneling with IPSec.
SSH (Secure Shell):
SSH is a cryptographic network protocol which is used for operating network services securely over the Internet. Likewise, it’s used in a VPN network for handling both tunnelings as well as encryption.
OpenVPN:
As the name Open implies, OpenVPN is an open-source VPN technology which is used widely for creating secure point-to-point or site-to-site connections while being configured and with remote access facilities. It’s one of the most popular and secure protocols, which offers protection like any other VPN protocol, but on a big scale.
If you have reached till here, then it’s alright to say that you might have gotten an idea about the VPN and its importance. If you’re choosing to go for a VPN, then its recommended not to go for free VPNs, as FREE is not always the right choice.